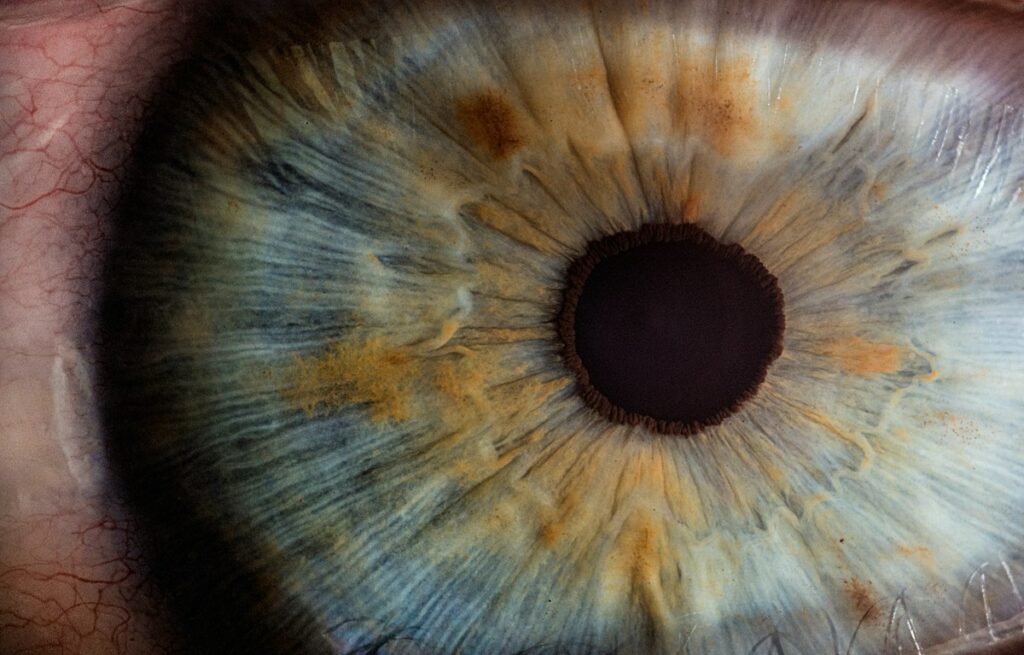
AMD stands for Age-related Macular Degeneration, which is a common eye condition and a leading cause of vision loss in people aged 50 and older. The macula is the central part of the retina, responsible for sharp, central vision needed for activities like reading and driving. AMD affects the macula, causing a loss of central vision while leaving peripheral vision intact.
There are two main types of AMD:
Dry AMD (Non-neovascular AMD): This is the more common form, characterized by the gradual breakdown of light-sensitive cells in the macula. Small yellow deposits called drusen may accumulate beneath the retina, leading to thinning and drying out of macular tissues.
Symptoms of dry AMD include:
- Blurred or distorted central vision
- Decreased contrast sensitivity
- Difficulty recognizing faces
- Need for brighter light when reading
- Increased difficulty adapting to low light conditions
Wet AMD (Neovascular AMD): This type is less common but more severe. It involves abnormal blood vessel growth beneath the retina, leaking blood and fluid, which can cause rapid and severe vision loss.
Symptoms of wet AMD can include:
- Sudden worsening or distortion of central vision
- Straight lines appearing wavy or crooked
- Blind spots or dark spots in central vision
- Decreased visual acuity
It’s important to note that AMD typically does not cause total blindness, as peripheral vision is usually unaffected. However, it can significantly impact daily activities that require central vision, such as reading, driving, and recognizing faces.
Regular eye exams are crucial for detecting AMD early, as early intervention can help slow its progression and preserve vision. If you’re experiencing any changes in your vision, especially central vision, it’s essential to consult an eye care professional promptly.